System solutions for Water treatment plants Nuremberg
Our product range
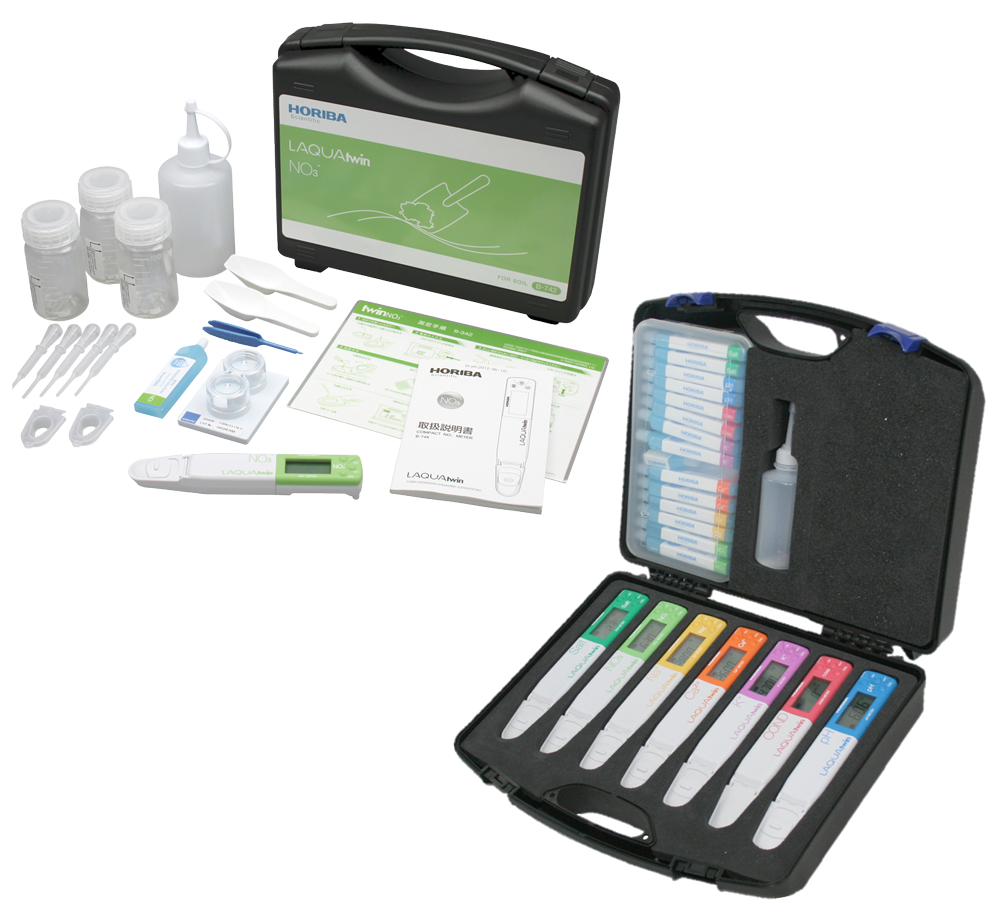
Pocket tester and analysis case
- Water and wastewater treatment: handheld meters are used to measure pH, conductivity, dissolved oxygen, ORP and other parameters in water and wastewater samples.
- Agriculture: Handheld meters are used to measure soil pH, nitrogen content, potassium content and other parameters in soil samples.
- Food industry: Handheld meters are used to measure pH, salt content and other parameters in food samples.
- Environmental analysis: Handheld meters are used to measure pH, conductivity, dissolved oxygen, ORP and other parameters in environmental samples such as soil, water and air.
There are many other applications for handheld meters, but these are some of the most common. Please note that the use of handheld analysers depends on the type of measurement and it is important to choose the right analyser for the application.
You also have the option of configuring your individual analysis case to customise your mobile laboratory to your specific application.
Some of the most common types of handheld meters are:
- pH testers: This type of handheld meter is used to measure the pH of liquids. They are available in different sizes and shapes and can be used for a variety of applications, such as water analysis, food and beverage analysis and agriculture.
- Conductivity testers: This type of handheld meter is used to measure the conductivity of liquids. They are useful for monitoring water quality and purity in industrial water treatment and agriculture.
- Oxygen testers: This type of handheld meter is used to measure the oxygen content in liquids. They are useful for monitoring bodies of water, drinking water and process water.
- Salinity testers: This type of handheld meter is used to measure the salinity of liquids. They are useful in monitoring salinity in seawater and in food and beverage analysis.
Advantages of hand-held measuring devices
Hand-held measuring devices are portable measuring devices that can be used to measure various parameters quickly and accurately. They have several advantages over stationary measuring devices:
- Mobility: handheld meters are small and lightweight and can be easily transported from one place to another. They are ideal for use in field research or in situations where a quick measurement is required.
- Easy to use: Handheld meters are easy to use and require no specialised training or knowledge. They are ideal for use by technicians or researchers who do not have extensive experience with measuring devices.
- Cost-effectiveness: Handheld meters are generally less expensive than stationary meters. They are ideal for use in situations where a limited budget is available.
- Fast measurements: Handheld meters can take measurements quickly and easily without the need for extensive equipment or a large laboratory. They are ideal for use in situations where a quick measurement is required.
It is important to choose the right meter for the application or parameter being analysed.
Mobile gas detectors
Would you like to use mobile gas detectors to detect specific sources of danger in an industrial environment? HeylNeomeris offers you the right sensor for your area of application.
Mobile gas detectors are used in companies to measure potentially hazardous gas concentrations in the air and detect them at an early stage. They are used to protect employees, the environment and to comply with safety standards.
The detectors are portable devices that can be carried by employees as required. They are battery-operated and have sensors that can detect different types of gases such as ozone, methane, hydrogen, etc.
Companies throughout Germany use mobile gas detectors in various areas, depending on the specific sources of danger. Mobile gas detectors are used, for example, in industrial plants. In factories and production facilities, the use of mobile gas detectors enables the detection of leaks or unusual gas concentrations in pipes, tanks or other systems.
The detectors can trigger audible and visual alarms if a dangerous gas concentration is detected. This allows employees to react quickly and take appropriate action, such as evacuating the area or shutting down equipment.
You can find a selection of our products (sensors and measuring devices) in our online shop under Gas measuring devices - Heyl Neomeris Shop
Can't find the gas detector you are looking for? Give us a call or contact us by e-mail or via our contact form. We will be happy to help you find a customised solution for your application.
Ozone generators
HeylNeomeris as your supplier for ozone generators - equipment technology for the disinfection of water and air as well as for the purification of process water in industry
Ozone generators are used to produce ozone and are extremely powerful and efficient. They are an important component of water treatment and in industry. Ozone generators are used in industrial water treatment, process water treatment and, in particular, in the pharmaceutical industry, where they are used to kill germs and disinfect water and air. Ozone generators therefore enable the disinfection of drinking water and swimming pool water, for example. The advantage of using ozone is its environmental friendliness, the short dwell time in the water and its neutral flavour.
You can find a selection of ozone generators in the HeylNeomeris product portfolio at Ozone and UV technology - Heyl Neomeris Shop .
If you have any questions, you can contact us by phone, e-mail or via our contact form. We look forward to your enquiry.
Residual ozone destroyer
Residual ozone destructors from HeylNeomeris for the reduction of excess ozone
Residual ozone destructors are devices that are used in water treatment to break down excess ozone. Ozone is a reactive gas that can be produced in the atmosphere as well as by some devices such as ozone generators. Ozone destructors destroy the ozone produced before it can be released into the environment.
They work by catalytic decomposition of ozone using special catalysts. Our system consists of a reactor housing, flow internals and droplet separators, Carulite 200 catalyst granulate and electrical trace heating. HeylNeomeris is a supplier of residual ozone neutralisers and offers you a broad product portfolio of catalytic residual ozone neutralisers.
You can configure and order your suitable residual ozone destroyer simply and easily via our online shop: Residual ozone destructors - Heyl Neomeris Shop
If you have any questions, please call us on +49 (0) 5121 7609-0. You can also send us an e-mail or use the contact form. We will take care of your request.
Test sets for hand analysis
HeylNeomeris specialises in the distribution of test kits for manual analyses, among other things.
Test kits for manual analyses are special kits or sets of tools, reagents and accessories that are used to carry out manual chemical and physical tests to determine the quality of drinking water.
In our product portfolio, we offer a variety of test kits in the field of pH value determination in water. Examples include the Testoval pH range 5.5 to 8 test kit and the Testoval pH range 8 to 12 test kit. In addition, the Testoval pH-Chlor DPD test kit can be used to measure both the pH value and the chlorine content in swimming pool water. In addition to the large selection of pH test kits, there is a wide range of test kits that are suitable for testing other relevant measurement parameters in drinking water, such as the Testoval aluminium colour comparison device, the polyamine test kit, etc. Our product portfolio also includes DUROGNOST limit value kits and DUROVAL drop count titration tests.
We are also happy to offer you our test kits with an OEM label. If you are interested, please contact us personally.
UV systems
HeylNeomeris as an expert and supplier of UV systems
UV systems are used in water treatment to kill microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, yeasts and parasites.The systems work by irradiating the water with ultraviolet light, which destroys the organisms' DNA and RNA and thus prevents them from reproducing. UV disinfection is an effective method of water treatment as it requires no chemical additives and produces no harmful by-products.
UV systems are ideal for monitoring the water quality of water treatment, water blending and drinking water systems.They are easy to install and maintain.However, a precise technical design of the UV system is required to ensure that the UV disinfection does not fail to be effective and that the number of microorganisms is reduced to the desired minimum.
The quality and safety of drinking and process water can be guaranteed with a UV system.You can find a selection of our range of UV systems at UV systems - Heyl Neomeris Shop. In the product area, you will find products for different areas of application. If you have any questions or need advice, please contact us by phone or e-mail.
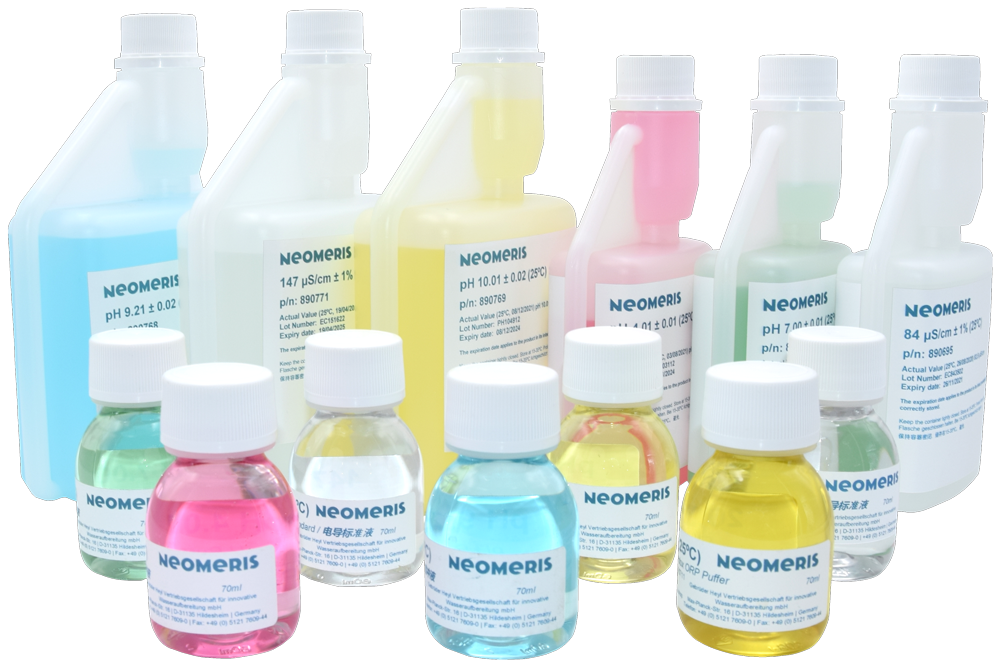
Calibration solutions
Calibration solutions are used to calibrate measuring instruments to a known reference to ensure that they provide accurate measurements.
HeylNeomeris offers a broad product portfolio of calibration solutions that are used in a wide range of applications, such as analytical chemistry, biochemistry, medicine, environmental analysis and the food industry.
There are various calibration methods for calibrating measuring devices.
A one-point calibration is a calibration method in which a measuring device is calibrated to a known reference by adjusting it to a solution with a known value. A two-point calibration is a calibration method in which a measuring device is calibrated to two known references by adapting it to solutions with two known values.
In one-point calibration, the meter is calibrated to a single point, while in two-point calibration, the meter is calibrated to two points. One-point calibration is easier and faster than two-point calibration, but two-point calibration is more accurate and reliable.
We offer a wide range of calibration solutions in different bottle sizes and disposable bags.
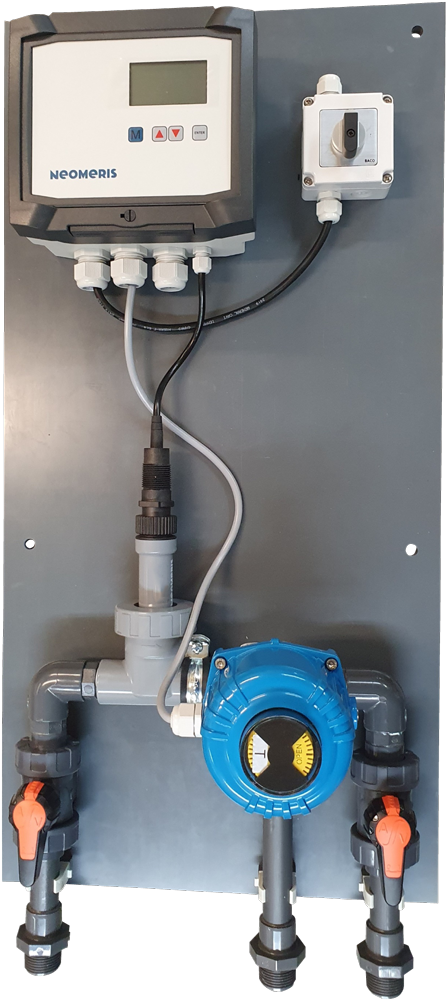
Multicontroller NeoTecMaster
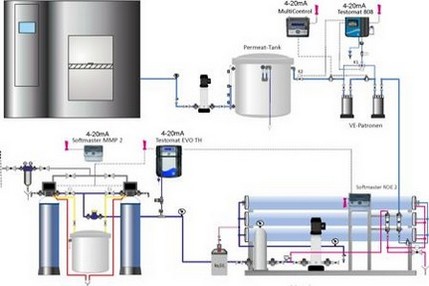
Gebrüder Heyl Vertriebsgesellschaft für innovative Wasseraufbereitung mbH has been recognised as a competent and reliable partner in professional water treatment for decades. Our technology enables us to monitor the most important parameters in complex industrial water treatment plants. HeylNeomeris is a modern, steadily growing supplier of measurement and control technology as well as system technology for industrial water treatment based in Hildesheim. Founded in 2009, we have followed a remarkable growth path. We are proud of our corporate culture, which emphasises innovation and progress. In addition to the development and expansion of the web and online shop matrix, we have developed our own PLC control system in just 9 months. Our daily work consists of constantly offering our customers the best application solution. Therefore, part of our continuous endeavour is to adapt, improve and expand our products to the changing market needs. For this reason, we have developed a manufacturer-open multi-parameter system, the NeoTecMaster®, within 9 months.
The NeoTecMaster® is suitable for monitoring water treatment plants and enables the networking of a wide variety of measuring systems and their integration into process automation. The multicontroller can implement customised extensions such as connection to the mobile phone network via GPRS or the integration of remote maintenance functions. The system is able to process up to eight measurement signals as standard. We can also configure your customised solution on request, as the multicontroller concept can be expanded to 20 parameters and more. The integration of the complete Heyl measurement technology is possible. The data received is displayed in the form of trend graphs.
The system is available in German, English, French, Mandarin (Chinese) and Russian.
Buffer solutions
Buffer solutions are solutions that keep the pH value stable when acids or bases are added. Buffer solutions are used, for example, in biochemistry, analytical chemistry or formulation.
The HeylNeomeris product portfolio offers a wide range of buffer solutions.
Examples include redox buffer solutions, which are used to keep the redox potential of a sample constant. A redox buffer consists of a redox pair consisting of an oxidation and a reduction component, which are mixed in a specific concentration to generate a defined redox potential. Buffer solutions therefore consist of a conjugate acid-base pair and can keep the pH value of a solution relatively stable. Redox buffer solutions are often used in biochemistry. They ensure that reactions take place at a constant pH value.
Another example of buffer solutions from our HeylNeomeris range are the pH buffer solutions. The pH value is an important parameter when analysing water. It indicates whether a solution is acidic, neutral or alkaline. In pure water or in neutral solutions, the pH value is 7. A pH value below 7 indicates an acidic solution, while a pH value above 7 indicates an alkaline solution. In water analysis, the pH value is measured to determine the quality of the water. The pH value is an important parameter in many technical systems, especially in water treatment. The pH value influences the chemical reactions that take place in the systems and can therefore affect the efficiency of the systems. For example, a pH value that is too low can lead to malfunctions in wastewater treatment plants, as it inhibits the growth of microorganisms that are responsible for the decomposition of organic substances. A pH value that is too high can lead to deposits and corrosion in pipework and other system components. In heating systems, a pH value that is too low can lead to corrosion and damage to the systems. In agriculture, a soil pH value that is too low can impair the growth of plants.
Choose the buffer solutions for your area of application from our comprehensive range, which are available in different bottle sizes or disposable bags.
Stationary gas detectors
HeylNeomeris as your supplier for stationary gas detectors - for measuring gas concentrations and for continuous ozone measurement
Stationary gas detectors are used in companies to ensure the safety of employees and systems. They measure the concentration of gases such as toxic gases, oxygen deficiency, flammable gases and vapours that cannot be detected by the human senses. The detectors alert the worker at an early stage and increase occupational safety.
Stationary measuring devices can be used for continuous ozone measurement in manufacturing companies. They measure the ozone concentration in the air in rooms with ozone generators, residual ozone destructors and ozone treatment systems.
Our ozone measurement device is the Gasmaster III, which is small, robust and ergonomic.
You can find more information about our product portfolio at Gas measuring devices - Heyl Neomeris Shop
We are also happy to advise you on the phone or by e-mail.
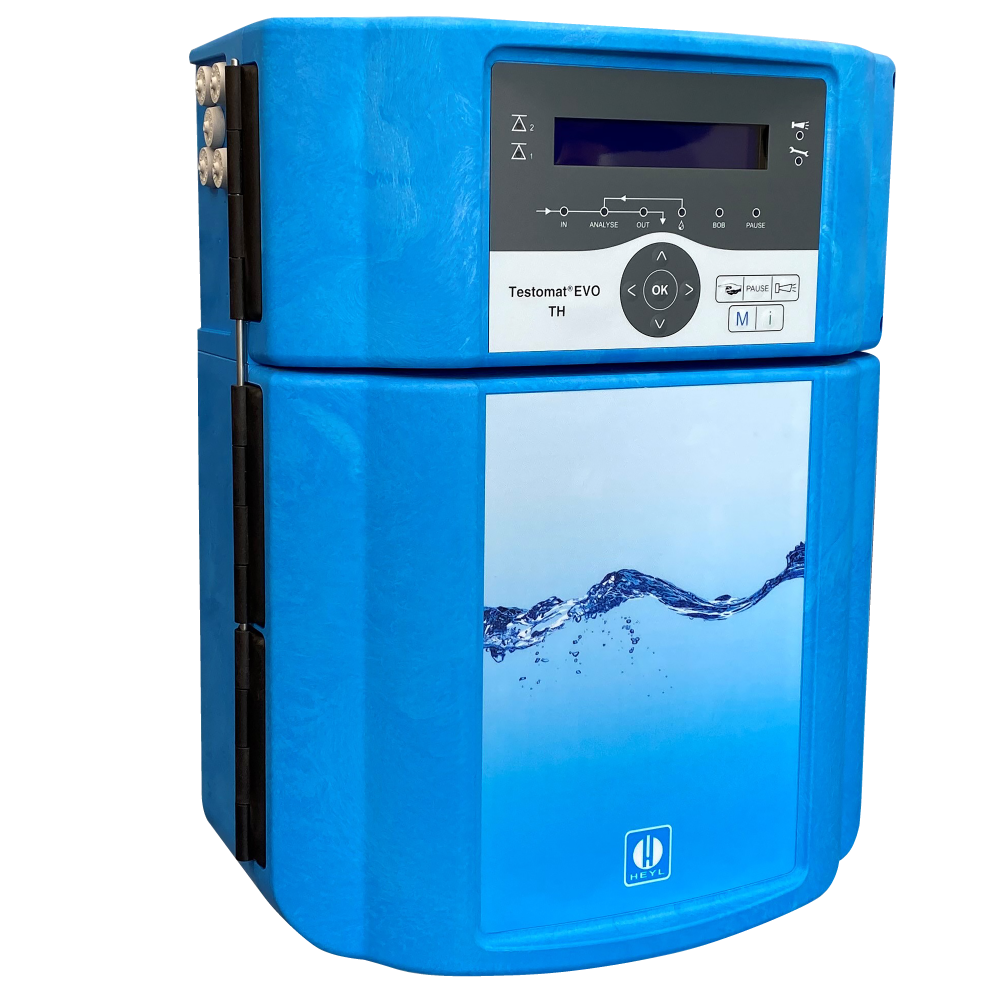
Testomats and associated chemistry
The HeylNeomeris product portfolio offers you an extensive selection of online analysers, the so-called Testomat®, for measuring relevant water parameters in various applications. Water hardness monitoring is particularly well known. In addition to monitoring various hardness parameters, we also offer you a large selection of Testomat devices for monitoring so-called non-hardness parameters, such as iron, silicate, bromine, chlorine, etc.
In the Testomat world of instruments you will find limit value measuring instruments (Testomat® 808) as well as actual value measuring instruments (e.g. Testomat 2000, Testomat EVO, Testomat LAB).
Our Testomat devices use indicators and reagents for the analysis process. The indicator is titrated drop by drop into the measuring chamber via the dosing pump until the colour change occurs or the colour intensity is measured. Only use the original manufacturer's indicators and reagents from Heyl for the precise measuring devices.
You can calculate your individual consumption of indicators and reagents with our online calculation tools:
- Indicator consumption calculator - Heyl Neomeris Shop
- Reagent consumption calculator - Heyl Neomeris Shop
You also have the option of ordering a subscription for your optimised consumption. Your added value: When you take out a subscription, you will receive a warranty extension for your new device from 24 to 36 months if you take it out within the first 3 months of purchase.
Tradition and future for innovative Water treatment plants Nuremberg
Measurement and control technology for water treatment plants drinking water, Nuremberg
.
Water treatment for a large city presents waterworks with a wide variety of challenges. First-class water quality can only be guaranteed with state-of-the-art control, measurement and regulation technology from suppliers such as Neomeris, Hildesheim.
Nuremberg, the Franconian metropolis, has a population of around 518,000, making it the second largest city in Bavaria and number 14 in Germany. The municipal supplier, N-ERGIE AG, supplies water not only to Nuremberg but also to the neighboring municipality of Schwaig. Every day, water flows into more than 70,000 drinking water connections and around 7,700 hydrants. In addition, N-ERGIE supplies large parts of northern Bavaria with electricity, natural gas, district heating and energy services.


The average daily consumption of drinking water in the supply area is around 95,000 cubic meters. In 2019, around 33 million cubic meters of drinking water flowed through the network to consumers.
Ultrapure water and process water treatment for Nuremberg
Pure Water and Process Water Treatment for Nuremberg
Meanwhile, a large city like Nuremberg needs more than just drinking water:
The food industry, beverage production, many research institutions or semiconductor manufacturers are supplied with ultrapure water. The pharmaceutical industry and medicine production need so-called pharma water. Ultrapure water and pharmaceutical water are also freed of substances that are considered healthy for human consumption, especially calcium and magnesium, in special water treatment plants using the most precise measurement and control technology.
Another product of modern water treatment plants is called process water. The same quality criteria do not apply here as for ultrapure or drinking water. But even process water must not contain any foreign substances that could damage production facilities – such as Legionella bacteria or dissolved heavy metals & silicates.
The number one topic in water treatment is, of course, healthy drinking water. For Nuremberg and Schwaig, it is largely pumped from groundwater wells. As it seeps into the depths, the raw water passes through natural filter layers, but also picks up minerals in the process. They are a major reason for the medium-hard water hardness of around 14 degrees German hardness. Nurembergers can enjoy their water without hesitation: The pure municipal tap water is good enough even for small babies.
Nuremberg water treatment: Where does Nuremberg's drinking water come from?
Water Treatment Nuremberg: History and High-Tech
About 70 percent of Nuremberg’s drinking water is sourced directly from the region and treated in the city’s five waterworks:
- The Erlenstegen/Eichelberg waterworks extracts raw water from around 100 wells in the Pegnitz Valley. The protected zone is water extraction and local recreation area.
- The Ranna waterworks is located in the Veldensteiner Forst. It draws its raw water for treatment from two nearby water extraction areas. Pumps it does not need, because the processed drinking water flows from the higher waterworks by gradient directly to Nuremberg.
- The Krämersweiher waterworks produces water from four deep wells, which are up to 148 meters deep. From Krämersweiher, the water is forwarded to the waterworks at the forester’s house.
- In the waterworks at the forester’s lodge, the water treatment runs without any use of chemicals. While many other waterworks, for example, require measuring devices for chemical parameters, the naturally occurring carbon dioxide (CO2) at the forester’s house is dissolved out of the water by aeration with finely filtered ambient air.
For almost 50 years, N-ERGIE receives part of the drinking water from the Zweckverband Wasserversorgung Fränkischer Wirtschaftsraum (WFW). Its groundwater extraction area is located around Genderkingen in the Danube Lechrain. After water treatment, the Nuremberg drinking water flows via feeder pipes into elevated tanks and from there in free fall into the supply network. The elevated tanks compensate for daily peaks and ensure a natural & stable pressure in the network.
Water treatment Nuremberg: history and high-tech
Today, water treatment plants work with high-precision measurement, control and regulation technology, with UV systems for disinfection, with online analysis devices such as Testomat or withozone generators or water hardness measuring devices. In earlier times, waterworks workers in Nuremberg could only dream of all that modern industrial water treatment entails. But it was precisely on the Pegnitz River that they set milestones.
Covered sewage ditches in the streets were mentioned as early as 1465. In 1854, there was a cholera epidemic in Nuremberg. As one of its causes, the city fathers realistically suspected the poor hygienic conditions. Thus, the city council decided to improve the water supply and organize it through a municipal enterprise. In 1865, the magistrate finally decided to complete the “Canalisation” project. In the same year, the first municipal waterworks opened. In 1893, the first of today’s five waterworks went into operation: the Krämersweiher water treatment plant.
After a major air raid in January 1945, the regulated supply of drinking water collapsed. However, by the end of the same year, the municipal utilities were able to fully resume operations and supply Nuremberg residents with sufficient drinking water. The most recent advance in water treatment for Nuremberg was the commissioning of the state-of-the-art Ranna filtration plant in 2016 (sources: N-ERGIE, nuernberg.de).
Neomeris measurement and control technology for water treatment, Nuremberg